Corrugated Pipe: Characteristics, Applications, and Maintenance
What is Corrugated Pipe?
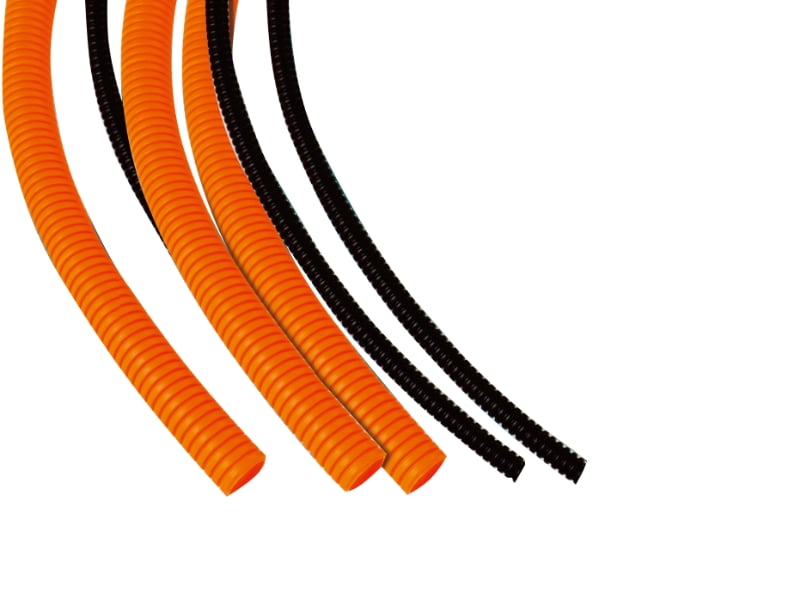
Corrugated Pipe is a flexible, lightweight piping solution characterized by its ridged (corrugated) exterior and smooth interior. This design provides exceptional strength-to-weight ratios while maintaining flexibility. Key technical specifications include:
Material Composition: Typically made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) with a density range of 0.941-0.965 g/cm³, polypropylene (PP), or polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Wall Structure: Features annular or helical corrugations with wall thicknesses ranging from 1.0mm to 6.0mm depending on diameter and pressure requirements.
Diameter Range: Available in sizes from 25mm (1") to 3000mm (118") for various applications.
Pressure Rating: Standard pipes withstand pressures of 15-60 psi, with reinforced versions handling up to 250 psi.
Temperature Range: HDPE variants maintain structural integrity between -40°C to 60°C (-40°F to 140°F).
Flexibility: Minimum bend radius of 20-30 times the pipe diameter without kinking.
The corrugated design provides a moment of inertia 3-5 times greater than smooth-walled pipes of equivalent material weight, offering superior resistance to external loads while using 20-30% less material than conventional piping solutions.

Key Applications of Corrugated Pipe
1. Drainage and Stormwater Management
Corrugated Pipes dominate subsurface drainage applications due to their:
High flow capacity (Manning's n value of 0.012-0.015 for smooth interiors)
Resistance to soil loads (ASTM D2412 pipe stiffness ≥ 320 kPa)
Perforation options (120° or 240° pattern with 5-10mm holes)
2. Electrical and Telecommunications Conduit
Used as protective raceways with:
EMI/RFI shielding capabilities (≥30 dB attenuation)
Crush resistance (≥2,500 N/100mm as per EN 2050)
Watertight joints (IP68 rating when properly sealed)
3. Agricultural Applications
Ideal for irrigation and subsurface drainage with:
Chemical resistance (pH range 2-12 compatibility)
UV stabilization (≥2% carbon black content for outdoor use)
Root penetration resistance (ASTM G160 12-month exposure rating)
4. Road and Railway Construction
Used as culverts and edge drains with:
AASHTO M252/M294 compliance
HS-20 loading capacity (minimum 1.5x safety factor)
Abrasion resistance (≤2mm wear after 100,000 wheel passes)
5. Ventilation Systems
Industrial applications leverage:
Low friction loss (Darcy-Weisbach f ≈ 0.02-0.025)
Fire ratings (UL94 V-0 flame spread classification)
Static dissipation (surface resistivity ≤10^9 ohms/sq)
Maintenance Best Practices
Inspection Protocols
Implement a regular inspection schedule with:
Visual checks every 6-12 months for surface cracks or deformation
CCTV inspections every 3-5 years for internal assessment
Structural testing (deflection ≤5% of diameter) after major soil movements
Cleaning Procedures
Maintain optimal flow capacity through:
Hydrojetting at 1,500-3,000 psi with 45° nozzles
Mechanical cleaning using poly brushes (≥80% pipe diameter)
Chemical treatment only with pH-neutral cleaners (6-8 pH range)
Joint and Connection Maintenance
Ensure system integrity by:
Checking coupling torque (25-35 Nm for typical 150mm connectors)
Replacing gaskets every 5-7 years or when compression set exceeds 15%
Applying lubricant (silicone-based, NSF 61 approved) during reassembly
Environmental Protection
Mitigate degradation factors:
UV protection with 2.5% minimum carbon black for exposed pipes
Rodent protection using 0.5mm stainless steel mesh at vulnerable entries
Thermal compensation loops every 30m for ΔT > 20°C applications
For buried installations, maintain minimum 300mm cover over pipes in vehicular areas and ensure proper bedding compaction (95% Standard Proctor density) to prevent excessive deflection. Always reference manufacturer-specific maintenance guidelines as material formulations vary significantly between products.



 English
English

