PVDF Heat Shrinkable Tubing: Properties, Applications, and Maintenance
Introduction
Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) heat shrinkable tubing is a high-performance polymer-based tubing widely used in industries requiring exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and electrical insulation. This tubing shrinks radially when exposed to heat, forming a tight, protective layer over components. Below, we explore its key characteristics, applications, and maintenance practices.
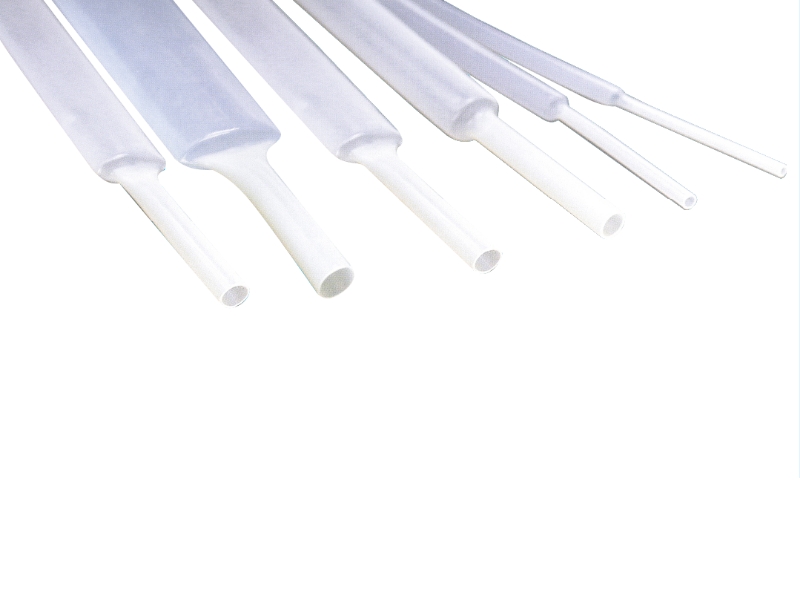

Key Properties of PVDF Heat Shrinkable Tubing
1. Chemical Resistance
PVDF tubing exhibits outstanding resistance to harsh chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents. It can withstand exposure to concentrated sulfuric acid (98%) at 23°C for 168 hours with less than 1% weight change, per ASTM D543 standards. Its resistance to halogenated hydrocarbons and oxidizing agents makes it ideal for chemical processing environments.
2. Thermal Stability
PVDF tubing operates effectively within a temperature range of -40°C to +150°C, with short-term exposure tolerance up to 175°C. Its melting point is approximately 177°C, and its thermal shrinkage ratio ranges from 30% to 50% when heated to 150°C for 10 minutes, ensuring a secure fit.
3. Electrical Insulation
With a dielectric strength of ≥20 kV/mm and volume resistivity of 1014–1015 Ω·cm, PVDF tubing provides excellent electrical insulation. Its low dielectric constant (6–9 at 1 MHz) minimizes signal loss in high-frequency applications.
4. Mechanical Strength
PVDF tubing has a tensile strength of 35–50 MPa and an elongation at break of 50–300% (ASTM D638). Its high abrasion resistance (Taber abrasion 2–5 mg/1000 cycles) ensures durability in demanding environments.
5. Flame Resistance
PVDF is inherently flame-retardant, achieving a UL94 V-0 rating with a limiting oxygen index (LOI) of 44%. It self-extinguishes within 10 seconds and emits minimal smoke when exposed to flames.
Applications of PVDF Heat Shrinkable Tubing
1. Chemical Processing
Used to protect sensors, valves, and piping systems in aggressive chemical environments, such as pharmaceutical and petrochemical plants.
2. Electrical and Electronics
Insulates high-voltage cables, battery terminals, and PCB components in aerospace, automotive, and energy storage systems.
3. Medical Devices
Due to its biocompatibility (ISO 10993-5 compliant), it is used in surgical tools and diagnostic equipment requiring sterilization (autoclavable at 121°C).
4. Oil and Gas
Protects subsea cables and downhole equipment from corrosive fluids and high-pressure conditions (up to 30 MPa).
5. Renewable Energy
Encapsulates photovoltaic junction boxes and wind turbine wiring, offering UV resistance (5000+ hours in QUV testing).
Maintenance Guidelines
1. Storage Conditions
Store in a cool (<25°C), dry environment away from direct sunlight. Relative humidity should be maintained below 60% to prevent premature aging.
2. Installation
Use a hot air gun or oven at 150–200°C for uniform shrinkage. Avoid open flames to prevent thermal degradation. Ensure a clean, debris-free surface before application.
3. Cleaning
Wipe with isopropyl alcohol (IPA) or deionized water. Avoid acetone or ketone-based solvents, which may cause swelling (swelling ratio <5% after 24-hour immersion).
4. Inspection
Regularly check for cracks, discoloration, or loss of flexibility. Replace tubing if hardness increases by more than 10 Shore D (per ASTM D2240).
5. Replacement Cycle
Under continuous service at 125°C, expect a lifespan of 8–10 years. In intermittent chemical exposure, inspect annually.



 English
English

