Fluororubber Heat Shrinkable Tube: Properties, Applications, and Maintenance
Introduction
Fluororubber Heat Shrinkable Tube is a specialized polymer material designed for high-performance insulation and protection in extreme environments. Composed of fluorinated elastomers, it offers exceptional resistance to heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress. This article explores its key characteristics, applications, and maintenance practices.
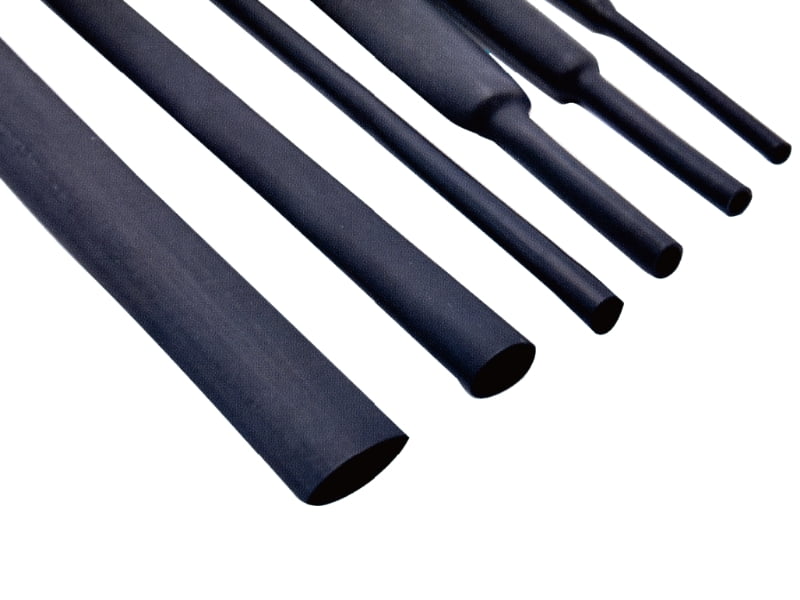

Key Properties and Technical Data
Fluororubber Heat Shrinkable Tubes exhibit the following properties with precise technical specifications:
Temperature Resistance: Operates continuously at -55°C to +200°C, with short-term tolerance up to 260°C (ASTM D2671).
Shrink Ratio: Standard ratios of 2:1 or 3:1, achieving full shrinkage at 175°C±10°C (IEC 60684-2).
Chemical Resistance: Withstands >500 hours of exposure to ASTM Oil #3 at 150°C with <5% volume swell (ASTM D471).
Dielectric Strength: >20 kV/mm (IEC 60243-1), with volume resistivity >10¹⁴ Ω·cm (ASTM D257).
Tensile Strength: 10-15 MPa with elongation at break of 150-300% (ASTM D412).
Flame Resistance: UL94 V-0 rated, with oxygen index >30% (ASTM D2863).
Application Scenarios
Fluororubber heat shrinkable tubes serve critical functions in multiple industries:
Aerospace
Used in jet engine wiring harnesses, protecting against hydraulic fluid exposure (MIL-H-5606) and thermal cycling from -65°C to 200°C. Complies with AMS-DTL-23053/4 standards for aerospace insulation.
Automotive
Protects high-voltage cabling in electric vehicles (600V DC systems), withstanding underhood temperatures up to 175°C (SAE J1654). Resistant to transmission fluids (Dexron VI) and brake fluids (DOT 4).
Industrial Equipment
Seals chemical processing equipment against corrosive media (pH 1-14), maintaining integrity at steam sterilization temperatures (121°C, 15 psi). Used in semiconductor manufacturing tools requiring Class 1 cleanroom compatibility.
Energy Sector
Insulates downhole cables in oil/gas extraction (API 17E), surviving H₂S environments (>1000 ppm) and 15,000 psi pressures. Solar panel junction boxes utilize UV-stabilized formulations (IEC 61215).
Maintenance Guidelines
Proper care ensures optimal performance and longevity:
Installation Procedures
Select tube diameter 20-30% larger than substrate (pre-shrink state)
Clean surfaces with isopropyl alcohol (≥99% purity)
Apply uniform heat using temperature-controlled hot air gun (175°C±10°C)
Maintain heating until complete shrinkage (typically 30-90 seconds)
Operational Maintenance
Inspect annually for cracks using 10x magnification (per MIL-STD-883 Method 2009.7)
Monitor for chemical degradation via hardness testing (Shore A ±5 points from baseline)
Verify dielectric properties with 500V megger testing (minimum 100MΩ)
Storage Conditions
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Temperature | 15-25°C (ASTM D4332) |
| Humidity | <60% RH |
| Light Exposure | UV-protected packaging |
| Shelf Life | 36 months from manufacture date |
Failure Analysis
Common issues and corrective actions:
Incomplete Shrinkage: Increase heat source temperature by 10°C increments (max 200°C)
Surface Cracking: Replace if cracks exceed 0.5mm depth (per SAE AS23053)
Adhesion Loss: Apply fluorosilane primer (0.1-0.3mm thickness) before reinstallation
Technical Standards Compliance
Fluororubber heat Shrink Tubes meet numerous international standards:
UL 224 (Extruded Insulating Tubing)
MIL-DTL-23053/5 (Military Specification)
ISO 1817 (Fluid Resistance Testing)
RoHS 2011/65/EU (Hazardous Substances)
Material Comparison
Performance versus alternative materials:
| Property | Fluororubber | Silicone | PVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Temp (°C) | 200 | 180 | 105 |
| Fuel Resistance | Excellent | Poor | Fair |
| Tensile (MPa) | 12 | 8 | 15 |
Advanced Formulations
Recent developments include:
Conductive variants with surface resistivity 10³-10⁵ Ω/sq (EMI shielding)
Adhesive-lined versions achieving 1.5N/mm peel strength (ASTM D903)
Thin-wall designs (0.3mm thickness) with 300% expansion ratio



 English
English

