Patterned Heat Shrink Tube: Characteristics, Applications, and Maintenance
What is Patterned Heat Shrink Tube?
Patterned Heat Shrink Tube is a specialized type of heat-shrinkable tubing that features distinct surface patterns (such as ribs, grooves, or textures) designed to enhance grip, flexibility, or identification. These tubes are manufactured from cross-linked polyolefin or other polymer materials with a shrink ratio ranging from 2:1 to 4:1, and they typically operate within a temperature range of -55°C to 125°C. The patterned surface increases surface area by 15-30% compared to smooth tubes, improving tactile properties and strain relief.
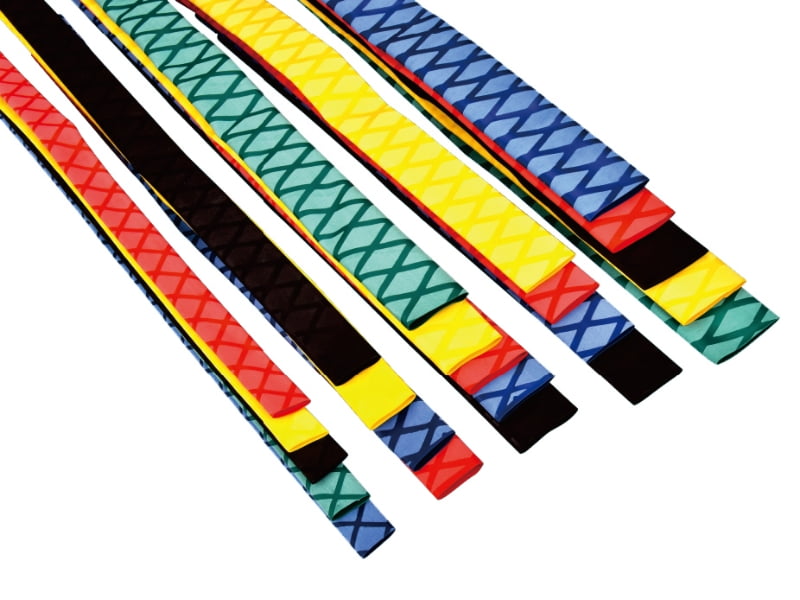

Key Technical Characteristics:
Dielectric Strength: 15-20 kV/mm (ASTM D149)
Tensile Strength: 10-17 MPa (ISO 37)
Elongation at Break: 300-500%
Flame Rating: UL224 VW-1 compliant
Shrink Temperature: 90°C (onset) to 135°C (full shrinkage)
Primary Applications
1. Industrial Cable Management:
Patterned tubes with ribbed surfaces are extensively used in heavy machinery where vibration resistance up to 20G is required. The texture prevents slippage in cable harnesses subjected to constant movement, such as in robotic arms or CNC equipment.
2. Aerospace Wiring:
In aircraft applications, these tubes meet SAE-AS23053/4 standards for weight reduction (specific gravity 0.95-1.2) while providing EMI shielding when combined with conductive patterns. The grooves allow for 30% faster installation in confined spaces.
3. Medical Devices:
Medical-grade patterned tubes with USP Class VI certification feature micro-patterns that enhance sterility by preventing fluid retention. Used in surgical tools and imaging equipment where 0.5mm wall thickness precision is critical.
4. Consumer Electronics:
Textured shrink tubes in mobile devices provide 5N/mm² crush resistance for internal wiring while the patterns serve as tactile indicators for service technicians. Common in laptop battery packs and wearable devices.
5. Automotive Systems:
Automotive patterned tubes withstand 125°C underhood temperatures (per SAE J2234) with color-coded grooves for wire identification. The patterns increase bending radius by 40% compared to smooth tubes.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation ensures optimal performance:
Cut tubes to length with 10-15mm overlap on connections
Use heat guns at 300-350°C or infrared shrink ovens
Apply heat evenly in circular motions at 50mm/s speed
For patterns requiring orientation, mark alignment before heating
Allow 2-3 minute cooling period before handling
Maintenance Procedures
Storage Conditions:
Store in original packaging at 15-25°C with 40-60% RH. Avoid UV exposure (shelf life reduces by 50% if stored in sunlight).
Cleaning Methods:
For general dirt: Use isopropyl alcohol (70% concentration) with lint-free cloth
For oil/grease: Apply hexane-free cleaners followed by water rinse
Never use abrasives that may damage patterns beyond 0.1mm depth
Inspection Protocol:
Quarterly inspections should check for:
Pattern deformation exceeding 10% of original dimensions
Cracks longer than 2mm in any direction
Discoloration indicating thermal degradation
Dielectric breakdown (test at 1.5x operating voltage)
Replacement Indicators:
Replace tubes when:
Shrinkage force drops below 0.3MPa (measured per ASTM D2671)
Surface patterns show >25% wear from original profile
Insulation resistance falls under 10^8 ohms (per IEC 60684-2)
Specialized Variants
Dual-Layer Patterned Tubes:
Combine inner adhesive (0.1-0.3mm thickness) with outer patterns for IP68 waterproofing. Used in marine applications with salt spray resistance >500 hours (ASTM B117).
High-Temperature Patterns:
Made with fluoropolymers (PTFE/PFA) for continuous 260°C operation. Patterns maintain integrity through 1000+ thermal cycles in chemical processing equipment.
EMI/RFI Shielding Tubes:
Integrate conductive patterns (surface resistivity<1 ohm="">) with nickel or copper elements. Provide 60dB attenuation from 10MHz-1GHz in aerospace electronics.



 English
English

